TOPIC 1: APPLICATIONS OF VECTORS
Scalar and Vector Quantities
Difference between Scalar and Vector Quantities
Distinguish between scalar and vector quantities
Scalar Quantities
These are physical quantities which have magnitude only. Examples of scalar quantities include mass, length, time, area, volume, density, distance, speed, electric current and specific heat capacity.
Vector Quantities
These are physical quantities which have both magnitude and direction. Examples of vector quantities include displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, pressure, retardation, and momentum.
Addition of Vectors Using Graphical Method
Add vectors using graphical method
Scalar physical quantities have magnitude only. Thus, they can be added, multiplied, divided, or subtracted from each other.
Example 1
If you add a volume of 40cm3 of water to a volume of 60cm3 of water, then you will get 100cm3of water.
Vector quantities are added by considering their directions. In this manner diagrams are important when adding two or more vectors.
Vectors Representation
A vector quantity can be represented on paper by a direct line segment.

- The length of the line segment represents the magnitude of a vector.
- The arrow head at the end represents the direction.
Methods of Vector Addition
There are two methods that are used to sum up two vectors:
- Triangle method
- Parallelogram method.
Triangle Method
A step-by-step method for applying the head-to-tail method to determine the sum of two or more vectors is given below.
1.Choose a scale and indicate it on a sheet of paper. The best choice of scale is one that will result in a diagram that is as large as possible, yet fits on the sheet of paper.
2.Pick a starting location and draw the first vectorto scalein the indicated direction. Label the magnitude and direction of the scale on the diagram (e.g., SCALE: 1 cm = 20 m).
3.Starting from where the head of the first vector ends, draw the second vectorto scalein the indicated direction. Label the magnitude and direction of this vector on the diagram.
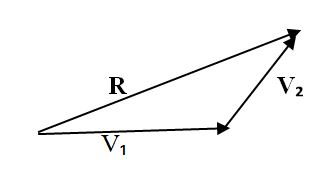
4.Draw the resultant from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector. Label this vector as Resultant or simply R.
5. Using a ruler, measure the length of the resultant and determine its magnitude by converting to real units using the scale (4.4 cm x 20 m/1 cm = 88 m).
6. Measure the direction of the resultant using the counterclockwise convention.
Resultant vector: This is the vector drawn from the starting point of the first vector to the end point of the second vector which is the sum of two vectors.
Where:
- V1 - First vector
- V2 - Second vector
- R - Resultant vector
Example 2
Suppose a man walks starting from point A, a distance of 20m due North, and then 15m due East. Find his new position from A.
Solution
Use scale
1CM Represents 5m
Thus
20m due to North Indicates 4 cm
15m due to East Indicates 3cm.
Demonstration
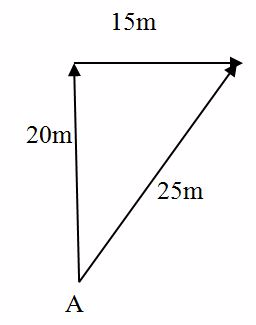
The position of D is represented by Vector AD of magnitude 25M or 5CM at angle of 36051”
Since
- Tan Q = (Opposite /Adjacent)
- Tan Q = 3cm /4cm
- Q = Tan -1 (3/4)
- Q = Tan -1(0.75)
- Q = 35º51”
The Resultant displacement is 25m ad direction Q = 36º51”
The Triangle and Parallelogram Laws of Forces
State the triangle and parallelogram laws of forces
Triangle Law of Forces
Triangle Law of Forces states that “If three forces are in equilibrium and two of the forces are represented in magnitude and direction by two sides of a triangle, then the third side of the triangle represents the third force called resultant force.”
Example 3
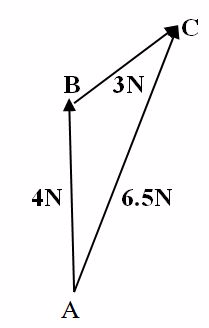
A block is pulled by a force of 4 N acting North wards and another force 3N acting North-East. Find resultant of these two forces.
Demonstration
Scale
1cm Represents 1N
Draw a line AB of 4cm to the North. Then, starting from B, the top vectorofAB, draw a line BC of 3 CM at 45oEast of North.
Join the line AC and measure the length (AC = 6.5 cm) which represents 6.5N. Hence, AC is the Resultant force of two forces 3N and 4N.
Parallelogram Method
In this method, the two Vectors are drawn (usually to scale) with a common starting point , If the lines representing the two vectors are made to be sides of a parallelogram, then the sum of the two vectors will be the diagonal of the parallelogram starting from the common point.
The Parallelogram Law states that “If two vectors are represented by the two sides given and the inclined angle between them, then the resultant of the two vectors will be represented by the diagonal from their common point of parallelogram formed by the two vectors”.
Example 4
Two forces AB and AD of magnitude 40N and 60N respectively, are pulling a body on a horizontal table. If the two forces make an angle of 30o between them find the resultant force on the body.
Solutiuon
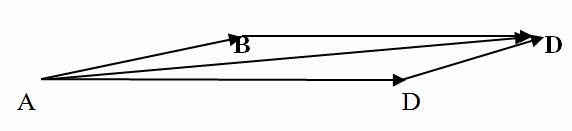
Choose a scale.
1cm represents10N
Draw a line AB of 4cm
Draw a line AD of 6cm.
Make an angle of 30o between AB and AD. Complete the parallelogram ABCD using the two sides AB and include angle 30O.
Draw the lineAC with a length of9.7 cm, which is equivalent to 97 N.
The lineAC of the parallelogram ABCD represents the resultant force of AB and AD in magnitude and direction.
Example 5
Two ropes, one 3m long and the other and 6m long, are tied to the ceiling and their free ends are pulled by a force of 100N. Find the tension in each rope if they make an angle of 30obetween them.
Solution
1cm represents 1N
Thus
3cm = represent 3m
6cm = represents 6m
Demonstration
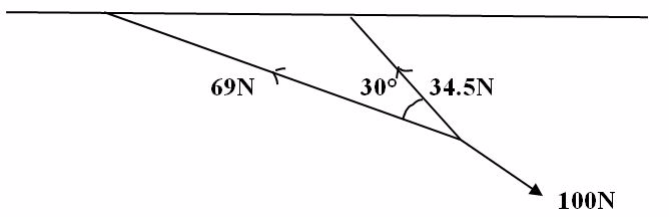
By using parallelogram method
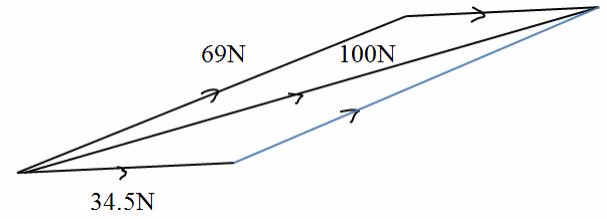
Tension, determined by parallelogram method, the length of diagonal using scale is 8.7 cm, which represents 100N force.
Thus.
Tension in 3m rope = 3 X 100 / 8.7 = 34.5N
Tension in 6m rope = 6 x 100 / 8.7 =69N
Tension force in 3m rope is 34.5N and in 6m rope is 69N.
Note: Equilibrant forces are those that act on a body at rest and counteract the force pushing or pulling the body in the opposite direction.
Relative Motion
The Concept of Relative Motion
Explain the concept of relative motion
Relative motion is the motion of the body relative to the moving observer.
The Relative Velocity of two Bodies
Calculate the relative velocity of two bodies
Relative velocity (Vr) is the velocity relative to the moving observer.
CASE 1: If a bus in overtaking another, a passenger (observer) in the slower bus sees the overtaking bus as moving with a very small velocity.
CASE 2: If the passenger was in a stationary bus, then the velocity of the overtaking bus would appear to be greater.
CASE 3: If the observer is not stationary, then to find the velocity of a body B relative to body A add velocity of B to A.
Example 6
If velocity of body B is VB and that of body A is VA, then the velocity of B with respect to A , the relative velocity VBA is Given by:
VBA = VB + (-VA)
That is
VBA = VB – VA
NOTE:The relative velocity can be obtained Graphically by applying the Triangle or parallelogram method.
For same direction
VrBA = VB - (+VA)
VrBA= VB – VA ___________________ (I)
For different direction
VrBA = VB – (-VA)
VrBA = VB + VA _______________________ (II)
Example 7
A man is swimming at 20 m/s across a river which is flowing at 10 m/s. Find the resultant velocity of the man and his course if the man attempted to swim perpendicular to the water current.
Solution
Scale
1cm represents 2m/s
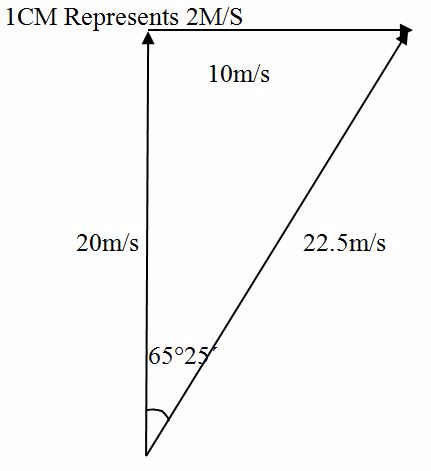
- The length of AC is 11.25 cm which is 22.5 m/s making an angle of 65º25’ with the water current.
- The diagonal AC represent (in magnitude and direction) the resultant velocity of the man.
The Concept of Relative Motion in Daily Life
Apply the concept of relative motion in daily life
Knowledge of relative motion is applied in many areas. In the Doppler effect, the received frequency depends on the relative velocity between the source and receiver. Friction force is determined by the relative motion between the surfaces in contact. Relative motions of the planets around the Sun cause the outer planets to appear as if they are moving backwards relative to stars in universe.
Resolution of Vectors
The Concept of Components of a Vector
Explain the concept of components of a vector
Components of a vector are vectors which when compounded or added, provides a single vector known as compounded vector.
Resolved vector is asingle vector which can be split up into component vectors.
Component vectors are vectors obtained after splitting up or dividing a single vector.
Resolution of a Vector into two Perpendicular Components
Resolve a vector into two perpendicular components
Components of a vector are divided into two parts:
- Horizontal component
- Vertical component
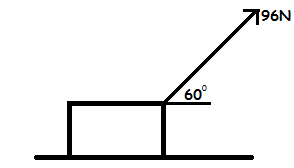
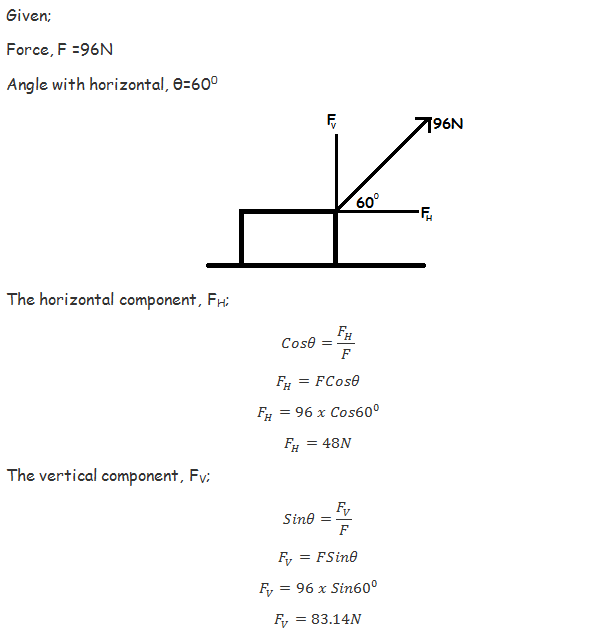
Consider the below diagram of force F which has been splitted into its vertical and horizontal components.
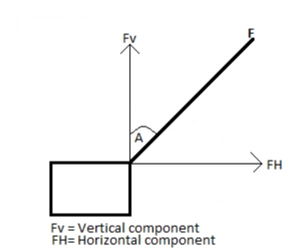
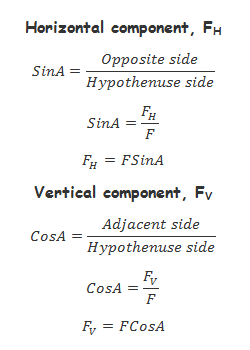
Note;The use of Sine or Cosine to find the components of the force depends on the position of the measured angle. The angle can be between the vertical component and the force OR between the horizontal component and the force.
Resolution of Vectors in Solving Problems
Apply resolution of vectors in solving problems
Example 8
Find the horizontal and vertical components of a force of 10N acting at 300 to the vertical.
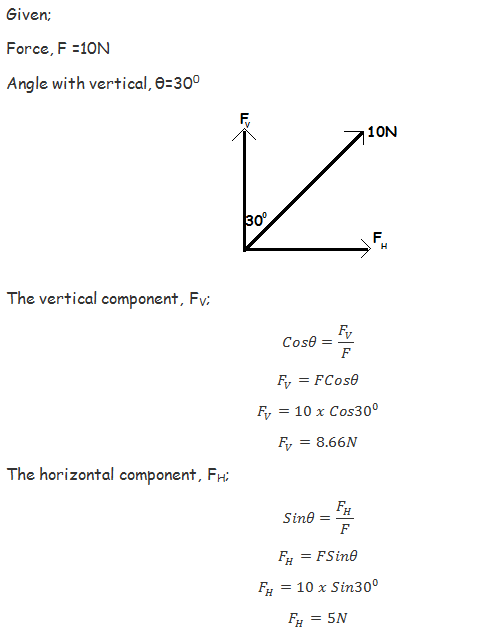
Example 9
Find the horizontal and vertical component of the force in the below diagram.